AP Business Writers ADVERTISING AP Business Writers Eds: Updates with close of US trading. With AP Photos. NEW YORK (AP) — Fears that Greece’s troubles could spread through the global financial system shook markets on Monday, driving U.S. stocks to
AP Business Writers
Eds: Updates with close of US trading. With AP Photos.
NEW YORK (AP) — Fears that Greece’s troubles could spread through the global financial system shook markets on Monday, driving U.S. stocks to their worst day of the year.
Investors fled from stocks in Europe and the U.S. and retreated to the safety of government bonds. Measures of volatility spiked. In many ways, it looked similar to previous episodes in Europe’s long-running debt crisis, except that this time, investors said, they weren’t quite as worried.
A series of events over the weekend left Greece perilously close to defaulting on its debts. Greece’s Prime Minister, Alexis Tsipras, said his government would hold a referendum on budget proposals made by the country’s lenders. European officials refused to extend the country’s bailout program, which expires on Tuesday, the same day it’s supposed to make a debt payment to the International Monetary Fund.
Jeff Carbone, a senior partner at Cornerstone Financial Partners, said the real worry isn’t so much Greece, a country with an economy roughly the size of Missouri’s. “It’s the contagion risk. If Greece goes, who’s next? This isn’t about Greece; it’s what happens next.”
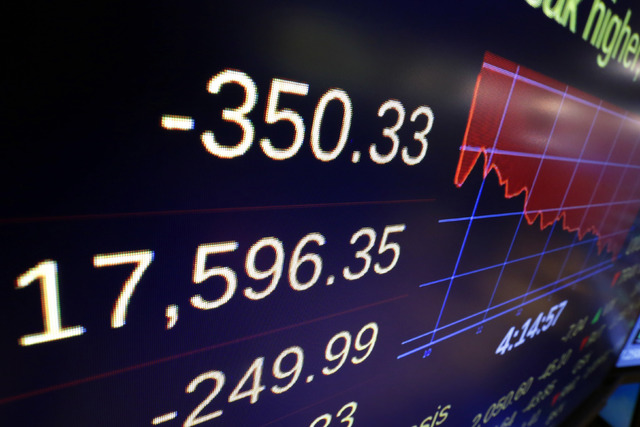
The Standard & Poor’s 500 index dropped 43.85 points, or 2.1 percent, to 2,057.64. The Dow Jones industrial average lost 350.33 points, or 2 percent, to 17,596.35, and the Nasdaq composite fell 122.04 points, or 2.4 percent, to 4,958.47.
The losses wiped out all the gains for the Dow and S&P 500 indexes this year.
In Europe, Germany’s DAX lost 3.6 percent while France’s CAC-40 lost 3.7 percent. The FTSE 100 index of leading British shares fell 2 percent. Greece’s stock market was closed. Investors bought German and British government bonds, which are seen as safe havens, and sold bonds issued by Greece’s government, sending those yields sharply higher.
“We are really looking at a situation where the market doesn’t know what the fallout is going to be,” said David Lafferty, chief market strategist at Natixis Global Asset Management. “But the U.S. market feels that it is relatively contained at this point.”
Over the weekend, the European Central Bank refused to extend its emergency support for Greece’s banking system. That prompted the Greek government to close banks and announce limits on withdrawals. Pictures of long lines at bank machines in Athens appeared on television screens around the world.
“Whenever you see any kind of bank line, there is in the back of investors’ mind the thought: ‘What if it spreads? What if people panic?’” said Karyn Cavanaugh, senior market strategist at Voya Investment Management. “What’s going on in Europe, of course it’s going to roil markets in the short term,” But for U.S. investors, she said, “the long-term impact is not that big of a deal.”
The last time Greece’s troubles shook U.S. markets, there were plenty of other problems. In 2012, Spain had entered a recession, and the worry was that it was too big of a country to rescue. Sputtering U.S. job growth added to the anxiety. That spring, the S&P 500 index lost 9.9 percent within two months. Investors sought safety in U.S. Treasury bonds, driving long-term interest to historic lows.
Back then, the fear was that a financial crisis would spread from Greece to the rest of Europe “because these economies were very fragile,” Cavanaugh said.
The rating agency Standard & Poor’s said Monday that it interprets the Greek government’s decision to hold a referendum as a sign that it will put “domestic politics over financial and economic stability, commercial debt payments and eurozone membership.” The agency says it now sees a 50-percent chance of Greece dropping the currency.
If Greece defaults and switches to a new currency, it’s sure to shake global financial markets. But the world is unlikely to see anything like the full-blown crisis of 2008. A few years ago, banks across Europe were loaded down with loans to the Greek government, corporations and banks. Things have changed since then.
“Today, the European banks have shed much of their Greek debt and they have significantly increased their capital,” says Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics. “A Greek default and exit from the euro zone would be devastating to Greece’s economy, but no one else’s. … The Greek standoff will be disconcerting to financial markets, but only temporarily.”
The European Central Bank is also ready to swing into action to prevent a panic. The ECB has already committed to buying 60 billion euros a month in corporate and government bonds to push down interest rates and help the European economy. It could buy even more, and flood financial markets with cash, to calm jittery European investors.
Bond price rose. The yield on the 10-year Treasury note fell to 2.33 percent from 2.47 percent late Friday, a big move. The euro rose to $1.1242 from $1.1160.
Gold edged up $5.80 to $1,179 an ounce, and silver slipped 7 cents to $15.66 an ounce. Copper edged up half a cent to $2.64 a pound.
Crude oil fell $1.30 to close at $58.33 a barrel in New York. Brent crude fell $1.25 to close at $62.01 a barrel in London.
In other trading in New York:
— Wholesale gasoline fell 1.9 cents to close at $2.030 a gallon.
— Heating oil fell 2.6 cents to close at $1.837 a gallon.
— Natural gas rose 3.2 cents to close at $2.805 per 1,000 cubic feet.
———
AP Economics Writer Paul Wiseman contributed to this report.